
On Sol 76, February 12, 2019, InSight’s Instrument Deployment Camera (IDC)
acquired a series of images showing deployment of the Heat Flow and Physical Properties Package (HP3). Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
NASA’s InSight Mars lander has successfully achieve a major milestone by deploying the German-supplied Heat Flow and Physical Properties Package (HP3).
Like the seismometer and Wind and Thermal Shield, the HP3 was placed on the surface of Mars by InSight’s robotic arm.
HP3 is designed to burrow down beneath the Red Planet’s topside — with its tether embedded with heat sensors — to a depth of 16 feet (five meters). The HP3 is slated to plow deeper than any previous arms, scoops, drills or probes before it.
Mole on Mars
HP3 can take Mars’ temperature to reveal how much heat is still flowing out of the interior of the planet.
Weighing a little over 6.5 pounds (about 3 kilograms) HP3’s “Mole” hammers itself under the surface. A maximum of 2 watts of power is available while burrowing underneath the surface.
The German Aerospace Center’s (DLR) HP3 heat flow probe has the Mole pulling a ribbon cable equipped with 14 temperature sensors behind it. Once the probe has reached its target depth, the temperature will be measured by all of the sensors every 15 minutes for several months.
Stable position
“We are pleased that the deployment of our HP³ experiment onto the Martian surface went so smoothly,” says Principal Investigator Tilman Spohn from the DLR Institute of Planetary Research in Berlin.
HP³ is now in a stable position approximately 5 feet (1.5 meters) from the lander.
“We hope that the Mole will not encounter any large rocks on its way into the subsurface,” Spohn says. The Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure (SEIS) was deployed previously – complete with an additional cover to protect it against wind and temperature fluctuations – at a similar distance from the InSight lander.
SEIS and HP³ are roughly 3 feet (one meter) apart.
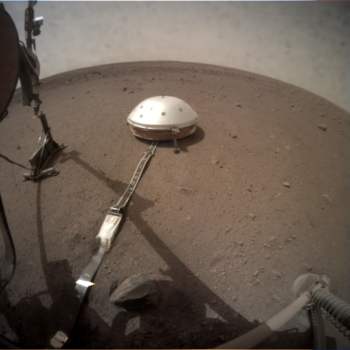
Sol 76 image taken by Instrument Context Camera (ICC) shows HP3 placed near seismometer. Photo acquired on February 12, 2019.
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech



