A Proton-M launch vehicle, with a Briz-M upper stage launched the EUTELSAT 5 West B communications satellite along with the Mission Extension Vehicle-1 (MEV-1) from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on October 9, 2019, local time.
If all goes well, Mission Extension Vehicle (MEV-1) will provide a satellite life-extension service by docking to the Intelsat 901 satellite in geosynchronous orbit to provide attitude and orbit control. Intelsat 901 was lofted back in mid-2001.
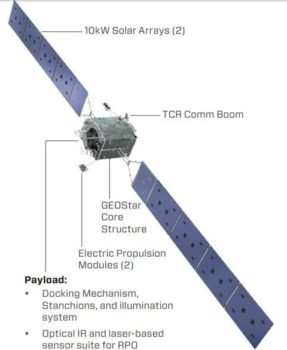
Rendezvous and docking
The MEV-1 mission is to extend the life of the Intelsat 901 satellite for five years, or an estimated 25 percent of its life, and also help mitigate the increasing congestion in Earth orbit.
Intelsat and MEV-1’s manufacturer — Northrop Grumman — will now begin to prepare for the most critical part of the mission—rendezvous and docking. To start, over the next three months, Northrop Grumman will perform orbit-raising maneuvers and raise the MEV-1 to 186 miles (300 kilometers) above Geo Synchronous Orbit.
During the same time, Intelsat will raise the position of Intelsat 901 from GEO to the docking orbit which will be about 186 miles (300 kilometers) higher than its traditional orbital location.
Abundance of caution
Multiple cameras, laser range-finders and on-board computers will allow MEV-1 to detect, track and rendezvous with Intelsat 901 at the docking orbit.
“As this is the first mission of its kind, out of an abundance of caution, we are operating these maneuvers above the normal orbital slot. This will ensure there is no disruption to any neighboring satellites,” explains Jean-Luc Froeliger, Vice President, Space Systems Engineering & Operations at Intelsat.
Docking mechanism
The final rendezvous between the craft will take place roughly three and a half months after MEV-1’s launch.
At that time, MEV-1 will insert a docking mechanism into Intelsat 901 apogee thruster and mechanically couple the two vehicles together. Once docked, the MEV will take over the attitude and orbit maintenance of the combined vehicle stack.
The combined MEV-1 and Intelsat 901 stack will be brought back to a geostationary orbit slot. Intelsat will then begin the transfer of services for their customers.
Keep-it-simple approach
“The MEV spacecraft provides rendezvous, proximity operations and docking features to enable a keep-it-simple approach to satellite life extension,” explains Northrop Grumman.
SpaceLogistics LLC, a wholly owned subsidiary of Northrop Grumman, is providing cooperative in-orbit satellite servicing to geosynchronous satellite operators. Their initial servicing vehicle is the now in orbit MEV.
For more information on launch of this milestone mission, go to: